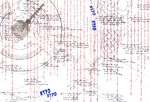
Columbus Circle, NYC II
2017-2020
Pen, pencil and acrylic paint on canvas
Dimensions: 180 x 130 cm
Details Text: esse #93
In the centre of New York City, in the centre of an iconic traffic circle named for him, Christopher Columbus stands flanked by the Time Warner Centre and the Trump International Hotel & Tower. This public circle and its monument are front and centre in the current debate surrounding the memorialisation of historic figures and periods, the need to question and examine the context from which they came, and ultimately the merits of their possible removal. This work nevertheless reveals those everyday moments of life—the mundane, the absurd, the humorous, the lonely, the dubious, and the spectacular—which occur in the shadow of this massive figure, and the even larger debate that surrounds him.
In 2020 I decided to rework this piece, adding a timeline of US events, from left to right, from the moment the Columbus statue was built in 1892 to September 2020. A timeline of 140 events in US history. It is a history of who has the power to write history; the moments when the US narrative changed and/or was rewritten. It is a history of empowerment and disempowerment, a history of US national identity and a charting of the country’s collective past.
HERE, THE EVENTS: 1892-2020
1892: The Columbus Monument is installed. Created by Italian sculptor Gaetano Russo.The statue was constructed with funds raised by Il Progresso, a New York City-based Italian-language newspaper
1892: Ellis Island, the United States’ first immigration station, opens in New York Harbor.
1892: Mass civil disobedience by Chinese immigrants defying the Geary Act requiring Chinese residents to carry photo identification proving that they were legal immigrants.
1903: W.E.B. Du Bois, “The Souls of Black Folk” is published
1906: President Theodore Roosevelt urges San Francisco to end the segregation of Japanese students from white students in San Francisco schools.
1907: Charles Curtis becomes the first Native American U.S. Senator.
1915: The film The Birth of a Nation is released, glorified lynching and the Reconstruction-era KKK.
1916: Margaret Sanger opens the first birth control clinic in the United States
1917: Congress passes the Espionage Act, making it illegal to mail literature “advocating or urging treason, insurrection, or forcible resistance” to the laws of the United States.
1917: The Immigration Act of 1917 is passed, establishing a literacy requirement for immigrants entering the country and halts immigration from most Asian countries.
1918: The Sedition Act is passed, targeting people who criticised the government, monitoring radicals and labor union leaders with the threat of deportation.
1919: The Texas Legislature investigates the ‘Texas Rangers’. Between 1910 and 1920, state law enforcement officers and Anglo vigilantes in the Texas-Mexico borderlands murdered hundreds of ethnic Mexican residents, American citizens and Mexican nationals alike.
1920: Ratification of the 19th Amendment guaranteeing all American women the right to vote.
1924: The Immigration Act of 1924 is passed limits the number of immigrants allowed into the United States yearly through nationality quotas.
1924: The Society for Human Rights is established in Chicago, the first recognised gay rights organisation in the US
1924: U.S. Congress passes the Indian Citizenship Act, granting citizenship to all Native Americans born in the territorial limits of the country.
1925: The KKK Marches in Washington
1933: President Franklin D. Roosevelt promises a "New Deal" to help America out of the Depression: Relief for the unemployed and poor, recovery of the economy back to normal levels, and reform of the financial system to prevent a repeat depression.
1933: Ratification of the 21st Amendment, ending national Prohibition
1935: Congress passed the Social Security Act, which for the first time provided Americans with unemployment, disability, pensions and aid for dependent mothers and children.
1936: Margaret Mitchell, “Gone With the Wind” in published
1938: House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC) is formed
1939: Nazi rally at Madison Square Garden
1939: John Steinbeck, “The Grapes of Wrath” is published
1940: Four Freedoms speech. In his State of the Union address President Franklin D. Roosevelt proposes four fundamental freedoms that people "everywhere in the world" ought to enjoy: Freedom of speech, Freedom of worship, Freedom from want and Freedom from fear.
1940: 26 states place restrictions, known as marriage bars, on employment of Married women.
1942: The Women’s Army Auxiliary Corps is created to enable women to serve in noncombat positions during World War II
1942: 120,000 Japanese Americans are imprisoned and relocated to internment camps
1946: “The Common Sense Book of Baby and Child Care” by pediatrician Benjamin Spock is published
1946: Milton Friedman is appointed professor of economics at the University of Chicago. Intellectual leader of the market-oriented Chicago School of Economics, his work reshapes conservative economic theory.
1946: The Hollywood blacklist is put in effect denying employment to entertainment industry professionals believed to be or to have been Communists or sympathisers.
1947: President Truman issues Executive Order 9835 which mandates that all federal employees be analysed to determine whether they are sufficiently loyal to the government.
1947: Congress passes the Taft-Hartley Act, designed by conservatives to create what they consider a proper balance between the rights of management and the rights of labor. Unions call it a slave labor law.
1948: Alfred C. Kinsey, “Sexual Behavior in the Human Male” is published
1948: Perfecto Martinez is confined as a “sexual psychopath”, charged with and convicted of the crime of “being an idle, lewd and dissolute person” for appearing in public dressed in female clothing.
1948: President Harry Truman issues Executive Order 9981 to end segregation in the Armed Services.
1948: The United States passes the nation’s first refugee and resettlement law to deal with the influx of Europeans after World War II.
1951: U.S. Supreme Court, in Dennis v. United States, rules that the free-speech rights of accused Communists could be restricted because their actions presented a clear and present danger to the government.
1951: California Supreme Court affirms the right of gay people to assemble (Black Cat Bar, San Francisco)
1952: The McCarran-Walter Act formally ends the exclusion of Asian immigrants to the United States.
1952: Christine Jorgensen an American transgender woman is was the first person to become widely known in the U.S. for having sex reassignment surgery.
1954: Brown v. Board of Education, Supreme Court rules that separating children in public schools on the basis of race was unconstitutional.
1955: Emmett Till, a 14-year-old from Chicago is brutally murdered in Mississippi for allegedly flirting with a white woman. His murderers are acquitted.
1955: The Daughters of Bilitis (DOB) is formed. The first lesbian civil and political rights organisation in the U.S.
1957: Nine black students known as the “Little Rock Nine” are blocked from integrating into Little Rock Central High School in Little Rock, Arkansas. President Dwight D. Eisenhower eventually sends federal troops.
1957: Russian-born philosopher Ayn Rand publishes Atlas Shrugged; promoting aggressive entrepreneurship and rejecting religion and altruism.
1958: Supreme Court decsionn, One, Inc. v. Olesen 355 U.S. 371, that pro-homosexual writing is not per se obscene.
1960: Six-year-old Ruby Bridges is escorted by four armed federal marshals as she becomes the first student to integrate William Frantz Elementary School in New Orleans.
1960: Harper Lee, “To Kill a Mockingbird” is published
1960: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approves the first commercially produced birth control pill in the world.
1961: Freedom riders, take bus trips through the American South to protest segregated bus terminals and attempted to use “whites-only” restrooms and lunch counters. The Freedom Rides were marked by horrific violence from white protestors.
1962: Rachel Carson, “Silent Spring” is published
1962: Illinois becomes the first state to legalise same-sex consensual sexual activity.
1963: President John F. Kennedy signs into law the Equal Pay Act, prohibiting sex-based wage discrimination between men and women performing the same job in the same workplace.
1963: Governor of Alabama, Democrat George Wallace, electrifies the white South by proclaiming "Segregation now, segregation tomorrow, segregation forever!"
1963: Approximately 250,000 people take part in The March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. Martin Luther King gives his “I Have A Dream” speech.
1963: James Baldwin, “The Fire Next Time” is published
1963: “The Feminine Mystique” by Betty Friedan is published, sparking the beginning of second-wave feminism in the U.S.
1964: Fannie Lou Hamer testifies before the DNC, demanding black political rights and boldly denouncing voter suppression and state-sanctioned violence.
1964: Democratic President Lyndon B. Johnson announces “The Great Society” a set of domestic programs whose goal was the total elimination of poverty and racial injustice.
1964: President Lyndon B. Johnson signs the Civil Rights Act into law. Title VII bans employment discrimination based on race, colour, sex, religion or national origin.
1964: The American Conservative Union, the oldest conservative lobbying organisation in the United States, is founded by William F. Buckley, Jr.
1965: Black religious leader Malcolm X is assassinated during a rally by members of the Nation of Islam.
1965: The Chicago Freedom Movement is formed to protest segregated housing, educational deficiencies, and employment and health disparities based on racism.
1965: The Immigration and Naturalization Act of 1965 abolishes an earlier quota system based on national origin and established a new immigration policy based on reuniting immigrant families and attracting skilled labor to the United States.
1967: The first bookstore devoted to gay and lesbian authors is founded, the Oscar Wilde Memorial Bookshop in NYC.
1968: The Indian Civil Rights Act is signed into law, granting Native American tribes many of the benefits included in the Bill of Rights.
1968: Martin Luther King, Jr. is assassinated in Memphis, Tennessee
1968: President Johnson signs the Civil Rights Act of 1968, also known as the Fair Housing Act, providing equal housing opportunity regardless of race, religion or national origin.
1968: TV journalist Walter Cronkite, "the most trusted man in America”, announces that it seemed "more certain than ever that the bloody experience of Vietnam is to end in a stalemate.”
1968: The Tet Offensive, a surprise attack launched by North Vietnam in the pre-dawn hours of Jan. 31. is a major turning point in the war. It shocked the American public into reality about the escalating conflict and led to President Johnson's decision not to seek re-election.
1969: The Stonewall riots, a series of spontaneous, violent demonstrations by members of the gay community against a police raid take place
1970: Dee Brown, “Bury My Heart at Wounded Knee” is published
1970: Kent State shootings occur during anti-Vietnam War student protests. 4 dead, 9 injured, shot by the Ohio National Guard.
1971: Nixon officially declares a “War on Drugs,” stating that drug abuse was “public enemy number one.”
1973: U.S. Supreme Court, in Roe v. Wade, declares that the Constitution protects a woman’s legal right to an abortion.
1980: Jerry Falwell, leader of the Moral Majority speech “We’re fighting a holy war”, starts the rise of the Christian right
1981: Sandra Day O’Connor is sworn in by President Ronald Reagan as the first woman to serve on the U.S. Supreme Court.
1982: "The Color Purple" by Alice Walker is published
1984: President Ronald Reagan reinforced and expanded many of Nixon’s War on Drugs policies.
1985: AIDS Project Los Angeles hosts the world's first AIDS Walk. President Ronald Reagan publicly mentions AIDS for the first time.
1986: President Ronald Reagan signs into law the Simpson-Mazzoli Act, granting amnesty to more than 3 million immigrants living illegally in the United States.
1986: Congress passed the Anti-Drug Abuse Act, establishing mandatory minimum prison sentences for certain drug offences. Five grams of crack triggered an automatic five-year sentence, while it took 500 grams of powder cocaine to merit the same sentence
1986: Congress enacts the Tax Reform Act of 1986, the 2nd of the "Reagan Tax Cuts". The act reduces the marginal income tax rate on the wealthiest Americans from 50% to 28%, and increases the marginal tax rate on the lowest-earning taxpayers from 10% to 15%
1986: Attorney Geoffrey Bowers is fired from the firm of Baker & McKenzie and sues. It is the first AIDS discrimination cases to go to a public hearing.
1989: Leonard Leo joins the Federalist Society, an organisation of conservatives and libertarians that advocates for a textualist and originalist interpretation of the United States Constitution. Leonard Leo is responsible, to a considerable extent, for choosing a third of the justices on the Supreme Court.
1988: The Rush Limbaugh Show debuts
1990: Conservative think tanks mobilise to challenge the legitimacy of global warming as a social problem. They challenge the scientific evidence, argue that global warming will have benefits, and warn that proposed solutions would do more harm than good.
1992: Unrest begins in South Central Los Angeles, after a trial jury acquits four LAPD officers for usage of excessive force in the arrest and beating of Rodney King.
1994: Present Bill Clinton signs the Violence Against Women Act, providing funding for programs that help victims of domestic violence, rape, sexual assault, stalking and other gender-related violence.
1994: Present Bill Clinton expands law enforcement, death penalty
1994: Republicans take control of the House of Representatives for the first time in 40 years
1995: A heat wave kills 739 in Chicago, bringing to attention the plight of the urban poor and the elderly in extreme weather conditions
1995: The Regents of the University of California voted to end affirmative action programs at all University of California campuses.
1996: Australian media mogul Rupert Murdoch launches Fox News Network
1998: Ban on use of affirmative action in admissions at the University of California go into effect. UC Berkeley has a 61% drop in admissions of African American, Latino/a and Native American students, and UCLA had a 36% decline.
1999: Columbine High School massacre
2001: 9/11
2001: President George W. Bush bans abortion aid
2001: The Bush administration rejects the Kyoto Protocol, an international treaty signed by 180 countries to reduce global warming that set limits on industrial emissions.
2001: Operation Enduring Freedom Begins
2001: Patriot Act is signed, increasing law enforcement agencies' ability to conduct searches in cases of suspected terrorism.
2002: Department of Homeland Security is established and takes over many immigration service and enforcement functions formerly performed by the Immigration and Naturalization Service.
2002: President Bush signs an education reform bill, “No Child Left Behind”, with bipartisan support.
2003: The Bureau of Immigration and Customs Enforcement, ICE is created.
2004: Abu Gharib Prison Abuse. American forces repeatedly torture Iraqi prisoners at the Abu Gharib prison.
2005: Antonio Ramon Villaraigosa became the first hispanic mayor of Los Angeles in 130 years
2006: The Supreme Court, in Hamadan vs Rumsfeld, rejects the position of the Bush Administration that they can hold terrorist without due process and the protection of the Geneva Accords.
2007: Virginia Tech Shooting — Seung -Hui Cho kills 32 students and wounds 17. It is the deadliest school shooting in US history. The US government passed the first gun control laws in a decade mandating improving state reporting
2008: Proposition 8 which prescribes that marriage is between a man and a woman in California is passed with 52.2% of the vote.
2009: Barak Obama is Inaugurated President on a platform of hope and change
2009: Sonia Sotomayor becomes the United States First Hispanic Supreme Court Justice.
2009: HIV travel ban. Obama lifts a 22-year-old ban that restricts those with HIV/AIDS from entering the United States.
2009: Hate Crimes Prevention Act becomes law to help jurisdictions to investigate and prosecute hate crimes more effectively.
2010: Congress passed the Fair Sentencing Act, which reduced the discrepancy between crack and powder cocaine offences from 100:1 to 18:1.
2010: President Obama signs Rosa’s Law, which changes the diction of federal statutes that use “mental retardation” to “intellectual disability.”
2010: “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell”. President Obama repeals the “Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell” policy, which allows people to openly be gay, lesbian, and bisexual while serving in the U.S. Armed Forces.
2011: Occupy Wall Street protest movement against economic inequality begins in Zuccotti Park
2012: Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting. 26 people killed, including 20 children between age six and seven.
2013: Edward Joseph Snowden, whistleblower, copies and leaks highly classified information from the National Security Agency (NSA).
2014: Black Lives Matter, the civil-rights protest movement, expands
2015: Supreme Court Ruling Makes Same-Sex Marriage a Right Nationwide.
2015: In his campaign launch speech Trump on Mexican immigrants: "They’re bringing drugs. They’re bringing crime. They’re rapists."
2016: “Make America Great Again”. Donald Trump is elected President in a stunning repudiation of the establishment.
2012: President Barack Obama signs Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) which temporarily shields some Dreamers from deportation, but doesn’t provide a path to citizenship.
2017: President Donald Trump issues executive order—“Protecting the Nation from Foreign Terrorist Entry into the United States”—aimed at curtailing travel and immigration from six majority Muslim countries (Chad, Iran, Libya, Syria, Yemen, Somalia) as well as North Korea and Venezuela. Both of these travel bans are challenged in state and federal courts.
2017: #MeToo movement against sexual abuse and sexual harassment, where people publicise allegations of sex crimes committed by powerful and/or prominent men, begins.
2017: The Unite the Right rally, a white supremacist and neo-Nazi rally, takes place in Charlottesville, Virginia
2018: The Trump administration’s policy ‘Family Separation’ and 'Zero Tolerance' at the Mexico/US border of is adopted.
2018: The Trump Administration announces that only 30,000 refugees will be allowed to enter the US in 2019, down from 45,000 in 2018.
2018: The National Memorial for Peace and Justice, a memorial to commemorate the victims of slavery, lynching and Jim Crow laws in the United States, opens in Montgomery, Alabama
2018: President Trump on immigrants: 'These aren't people. These are animals.’
2020: US House passes anti-lynching law, over 100 years after first attempt.
2020: House-passed anti-lynching bill doesn’t pass the Senate. Republicans argued anti-lynching legislation drafted too broadly
2020: President Trump tweets that painting Black Lives Matter on street would be "symbol of hate”
2020 President Trump issues an order to purge the federal government of racial sensitivity training that his White House called “divisive, anti-American propaganda.”
| |



|

